Using red seaweed-derived membranes as electrolytes
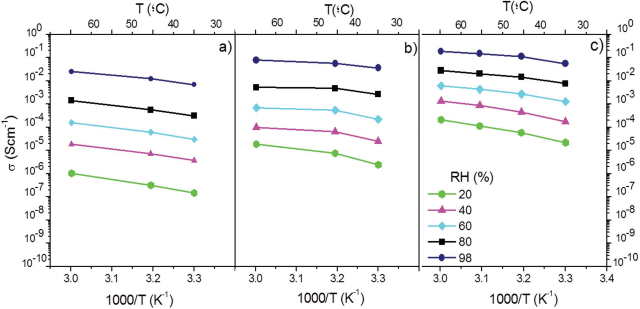
Green electrolytes composed of kappa-carrageenan (κ-Cg), 1-butyl-3-methyl- 1H-imidazolium chloride ([Bmim]Cl) ionic liquid, and glycerol (Gly) are prepared in aqueous solution using a simple, clean, fast and low-cost procedure. A flexible membrane incorporating 50% wt [Bmim]Cl and 50% wt Gly with respect to κ-Cg exhibits the highest ionic conductivity values (8.47 × 10−4/2.45 × 10−3 S cm−1 at 20/66 °C, under anhydrous conditions, and 5.49 × 10−2/0.186 S cm−1 at 30/60 °C, at a relative humidity of 98%). Tests of room temperature air/hydrogen fuel cells incorporating κ-Cg, κ-Cg/Gly, and κ-Cg/ Gly/[Bmim]Cl membranes demonstrate that these predominantly protonic conductors electrolytes are particularly well suited for the design and fabrication of eco-friendly electrochemical devices whose operation does not require the flow of gases and does not lead to water formation. These new materials have excellent application prospects in high performance (flexible) energy storage devices (supercapacitors and batteries) and electrochromic devices.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adsu.201700070
Autores: Sílvia C. Nunes, Rui F. P. Pereira, Nuno Sousa, Maria M. Silva, Paulo Almeida, Filipe M. L. Figueiredo, and Verónica de Zea Bermudez